Hexagonal architecture
general idea
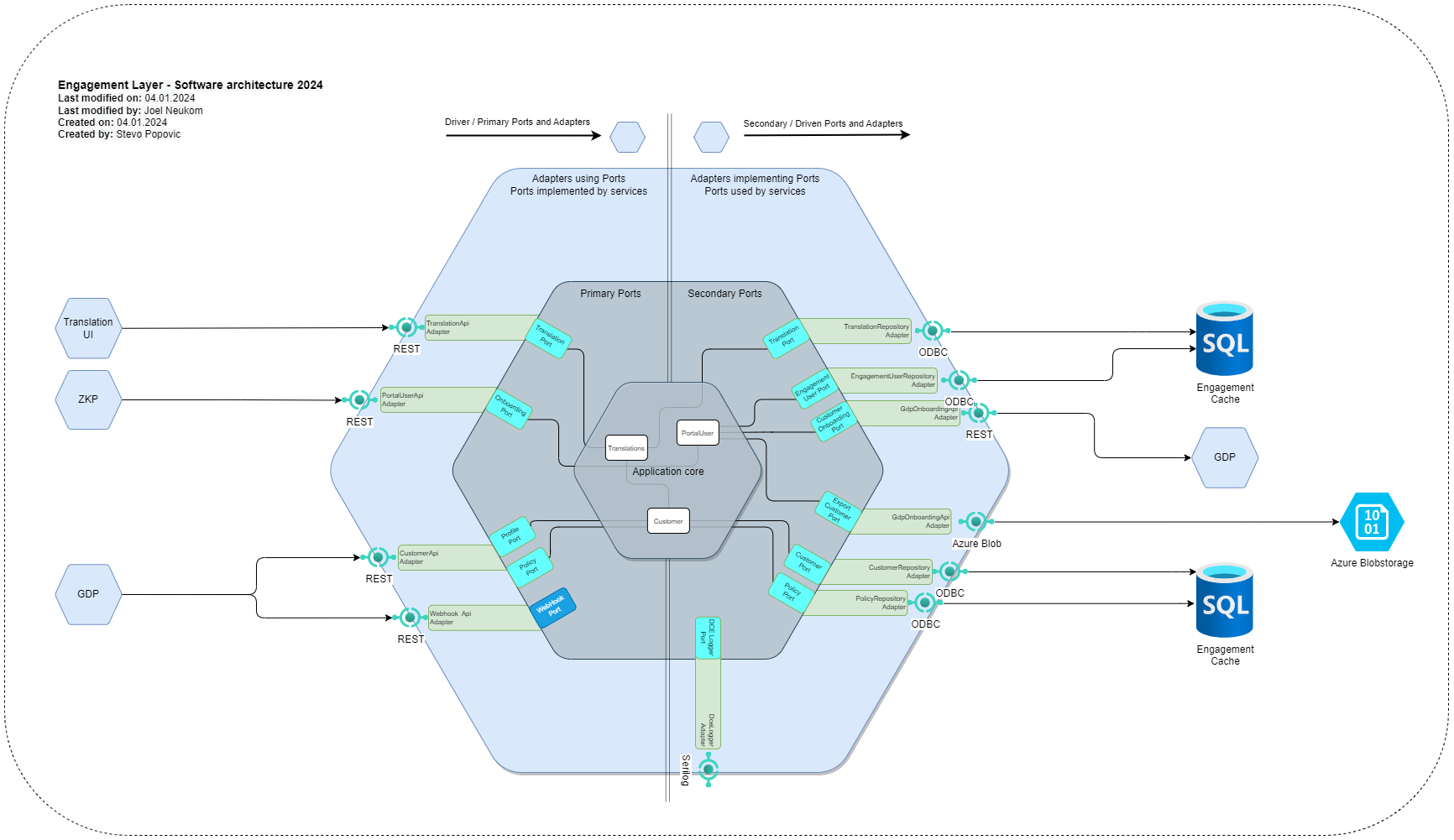
You define your application structure like this:
- Core
- DrivingPorts
- DrivenPorts
- Features (Business logic)
- Adapters
- DrivingAdapters
- DrivenAdapters
- Setup (Config, Logging, Startup, Settings etc.)
Where Driving/Driven Ports are interfaces (written in “core domain language”). And the Driving/Driven Adapter are the implementations of these ports.
Advantages
You can define the interfaces how to talk with the business logic on the core of the application. So the ports still “talks” in business logic language from the core and every adapter needs to adhere to it.
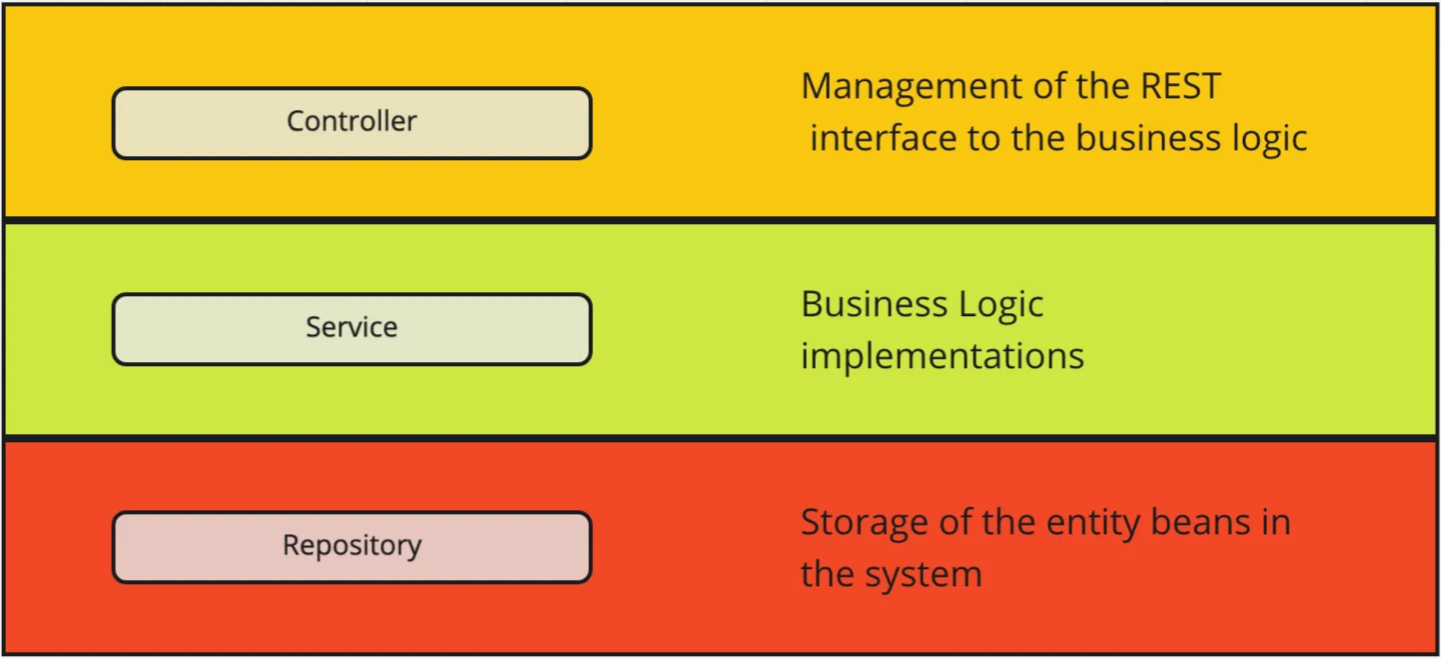
A 3 tier architecture follows the same principle, as for example @Repositories shall depend on models specified in the business layer. So it is the concern of the Repository to translate a “Customer” model to “CustomerDao” model And it is the concern of the Controller to translate a “Customer” model to “CustomerDto” model.
Though the missing part in 3tier architecture is you don’t have a name for these interfaces (ports).