SC-100 certification
SC-100: Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
https://aka.ms/courseSC-100
Day 1
Zero Trust Security
Core principle: Always verify, least privilege, assume breach.
6 pillars of Zero Trust
- Identity
- Endpoints
- Network
- Applications
- Data
- Infrastructure
Zero trust is a journey, not a product; no single tool can “enable” it.
Frameworks
- Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF): Guides cloud migration, including strategy, planning, readiness, and adoption. Landing zones are critical for scalable, secure cloud environments.
- Well-Architected Framework (WAF): Focuses on reliability, security, cost optimization, operational excellence, and performance efficiency. Trade-offs between pillars discussed.
- Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture (MCRA): Comprehensive reference library for security design, including anti-patterns, tool mapping, and modernization strategies. https://aka.ms/MCRA
- Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark (MCSB): Prioritized security controls for Azure and multi-cloud, mapped to industry standards. https://aka.ms/mcsb
Risk Management & Best Practices
Risk assessment: Impact vs. likelihood, not all risks can or should be eliminated. Importance of patching, balancing operational and security risks. Anti-patterns: Documented in the Cloud Adoption Framework, but not exhaustive.
Technical Tools & Operations
Azure Advisor: Provides recommendations aligned with the Well-Architected Framework. Landing zones: Templates and deployment scripts available for scalable Azure environments. SIEM/SOAR: Sentinel, Defender XDR, and integration with MITRE ATT&CK (https://attack.mitre.org/) for incident detection and response.
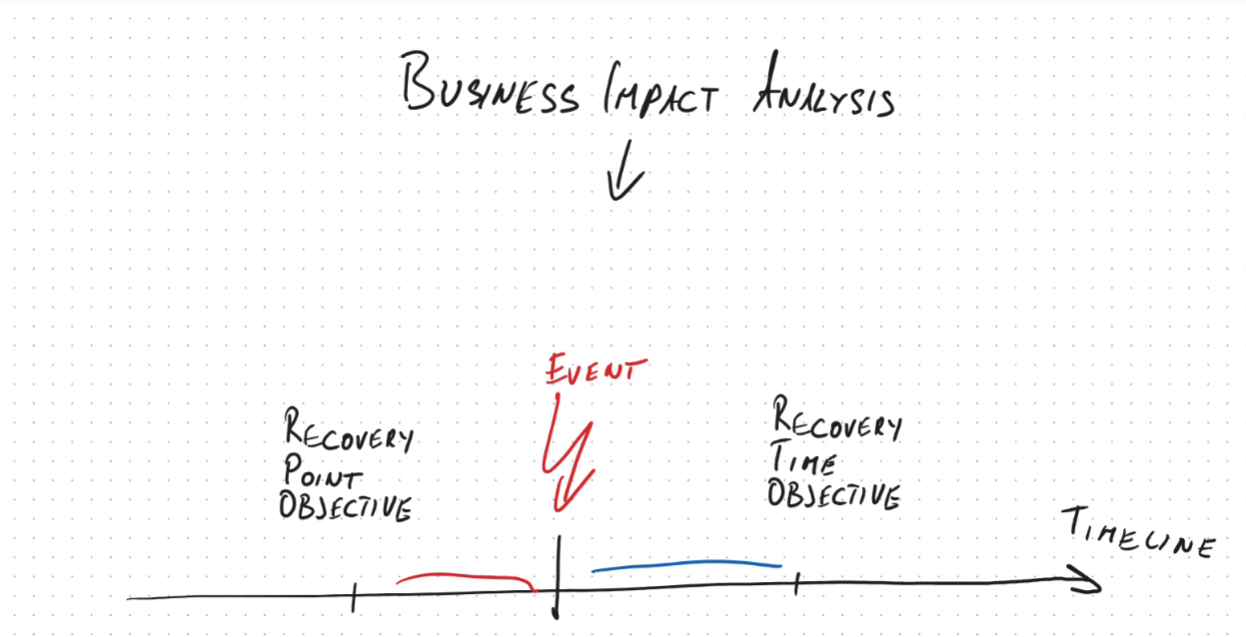
Ransomware & Resilience
Modern ransomware attacks involve both encryption and data exfiltration/extortion. Defense: Immutable backups, data classification, encryption, and incident response planning. Business continuity: Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are key metrics.